Google Algorithm Updates Cheat Sheet
Your ultimate guide to major Google penalties & algo changes

Google rolls out algorithm updates once or twice every month (and that's just the ones we know about!), but not all of them have an equally strong impact on the SERPs. To help you make sense of Google's major algo changes in the past years, I've put up a cheat sheet with the most important updates and penalties rolled out in the recent years, along with a list of hazards and prevention tips for each.
Contents
2) Click the Update visits button in Rank Tracker's top menu, and enter your Google Analytics credentials to sync your account with the tool.
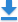
3) In the lower part of your Rank Tracker dashboard, switch to the Organic Traffic tab.
The dotted lines over your graph mark the dates of major Google algo updates. Examine the graph to see if any drops (or spikes!) in visits correlate with the updates. Hover your mouse over any of the lines to see what the update was.
Did any of the updates impact your organic traffic in any way? Read on to find out what each of the updates was about, what the main hazards are, and how you can keep your site safe.
1. Panda

Launched: Feb 24, 2011
Rollouts: ~monthly
Goal: De-rank sites with low-quality content
Rollouts: ~monthly
Goal: De-rank sites with low-quality content
Hazards
- Duplicate content
- Plagiarism
- Thin content
- User-generated spam
- Keyword stuffing
- Poor user experience
How to stay safe
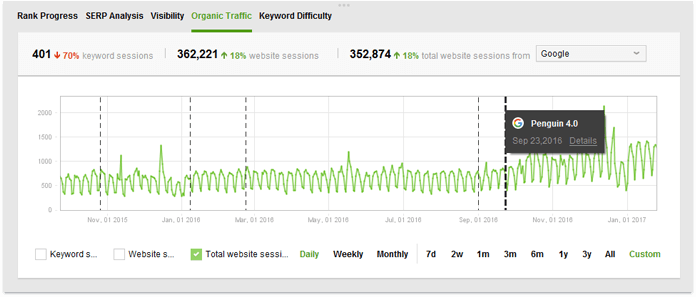
1. Check for duplicate content across your site. Internally duplicated content is one of the most common Panda triggers, so it's recommended that you run regular site audits to make sure no duplication issues are found. You can do it with SEO PowerSuite's Website Auditor (if you have a small site with under 500 resources, the free version should be enough; for bigger websites, you'll need a WebSite Auditor license).To start the check, launch WebSite Auditor and create a project for your site. Hang in a moment until the app completes the crawl. When done, pay attention to the on-page section of SEO factors on the left, especially Duplicate titles and Duplicate meta descriptions. If any of those have an Error status, click on the problematic factor to see a full list of pages with duplicate titles/descriptions.
If for some reason you can't take down the duplicate pages, use a 301 redirect or canonical tag; alternatively, you can block the pages from indexing with robots.txt or the noindex meta tag.
2. Check for plagiarism. External duplication is another Panda trigger. If you suspect that some of your pages may be duplicated externally, it's a good idea to check them with Copyscape. Copyscape gives some of its data for free (for instance, it lets you compare two specific URLs), but for a comprehensive check, you may need a paid account.
Many industries (like online stores with thousands of product pages) cannot always have 100% unique content. If you run an e-commerce site, try to use original images where you can, and utilize user reviews to make your product descriptions stand out from the crowd.
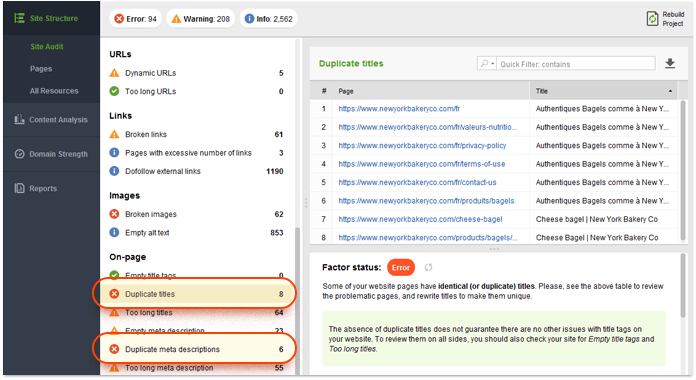
3. Identify thin content. Thin content is a bit of a vague term, but it's generally used to describe an inadequate amount of unique content on a page. Often, thin content pages are pages with low word count that are filled with ads, affiliate links, etc., and provide little original value. If you feel thin content could be a problem on your site, it's a good idea to measure it in terms of word count and the number of outgoing links on the page.
To check for thin content, navigate to the Pages module in your WebSite Auditor project. Locate the Word count column (if it's not there, right-click the header of any column to enter the workspace editing mode, and add the Word count column to your active columns). Next, sort the pages by their word count by clicking on the column's header to instantly spot the ones with very little content.
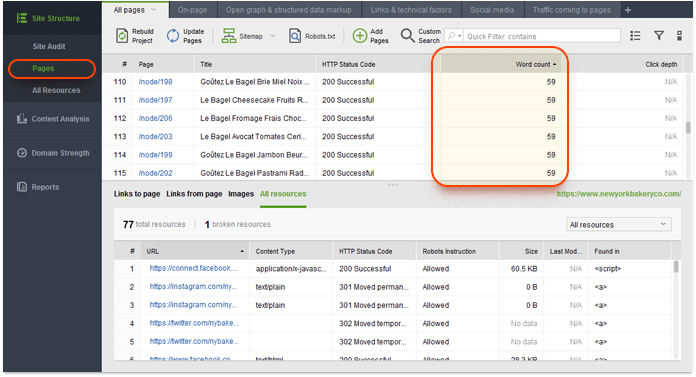
Next, switch to the Links tab and examine the External links column, showing the number of outgoing external links on the page. You can sort your pages by this column as well by clicking on its header. You may also want to add the Word count column to this workspace to see the correlation between outgoing links and word count on each of your pages. Watch out for pages with little content and a substantial number of outgoing links.
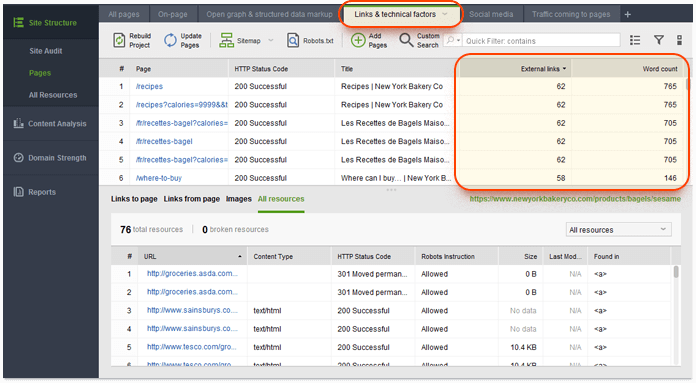
Mind that a "desirable" word count on any page is tied to the purpose of the page and the keywords that page is targeting. E.g. for queries that imply the searcher is looking for quick information ("what's the capital of Nigeria", "gas stations in Las Vegas"), pages with a hundred words of content can do exceptionally well on Google. The same goes for searchers looking for videos or pictures. But if those are not the queries you're targeting, too many thin content pages (<250 words) may get you in trouble.
As for outgoing links, Google recommends keeping the total number of links on every page under 100 as a rule of thumb. So if you spot a page with under 250 words of content and over 100 links, that's a pretty solid indicator of a thin content page.
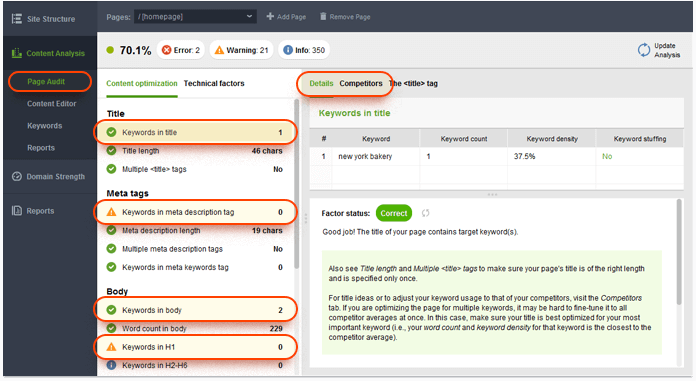
4. Audit your site for keyword stuffing. Keyword stuffing is a term used to describe over-optimization of a given page element for a keyword. To figure out if there are keyword stuffing issues on your pages, it's a good idea to look at your top ranking competitors' pages (that's exactly what SEO PowerSuite's WebSite Auditor uses in its Keyword Stuffing formula, in addition to the general SEO best practices).
In your WebSite Auditor project, go to Content Analysis, and add the page you'd like to analyze. Enter the keywords you're targeting with this page, and let the tool run a quick audit. When the audit is complete, pay attention to Keywords in title, Keywords in meta description, Keywords in body, and Keywords in H1. Click through these factors one by one, and have a look at the Keyword stuffing column. You'll see a Yes value here if you're overusing your keywords in any of these page elements. To see how your top competitors are using keywords, switch to the Competitors tab.
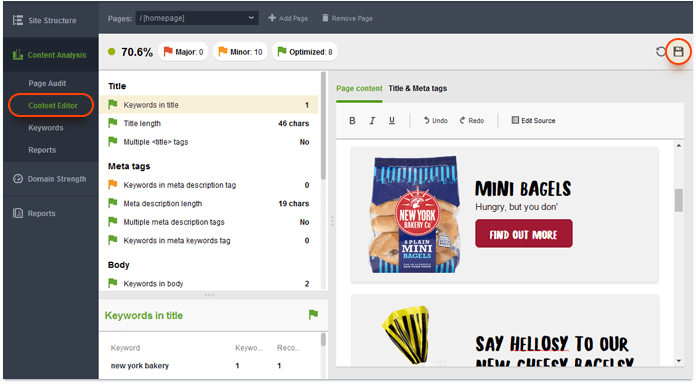
5. Fix the problems you find. Once you've identified the Panda-prone vulnerabilities, try to fix them as soon as you can to prevent being hit by the next Panda iteration (or to recover quickly if you've been penalized). You can edit your pages right in WebSite Auditor if you go to Content Analysis > Content Editor. Here, you can edit your content in a WYSIWYG editor, HTML, and play around with your titles and meta description in a user-friendly editor with a Google snippet preview. On the left, the on-page factors will recalculate as you type. Once you've made the necessary changes, hit the Save button to save the upload-ready HTML file to your hard drive.
2. Penguin

Launched: April 24, 2012
Rollouts: May 25, 2012; Oct 5, 2012; May 22, 2013; Oct 4, 2013; Oct 17, 2014; September 27, 2016; October 6, 2016; real-time since
Goal: De-rank sites with spammy, manipulative link profiles
Rollouts: May 25, 2012; Oct 5, 2012; May 22, 2013; Oct 4, 2013; Oct 17, 2014; September 27, 2016; October 6, 2016; real-time since
Goal: De-rank sites with spammy, manipulative link profiles
Hazards
- Links coming from poor quality, "spammy" sites
- Links coming from sites created purely for SEO link building (PBNs)
- Links coming from topically irrelevant sites
- Paid links
- Links with overly optimized anchor text
How to stay safe
1. Monitor link profile growth. Google isn't likely to penalize a site for one or two spammy links, but a sudden influx of toxic backlinks could be a problem. Look out for any unusual spikes in your link profile, and always look into the new links you acquire. By creating a project for your site in SEO PowerSuite's SEO SpyGlass, you'll instantly see progress graphs for both the number of links in your profile, and the number of referring domains. An unusual spike in either of those graphs is reason enough to look into the links that your site suddenly gained.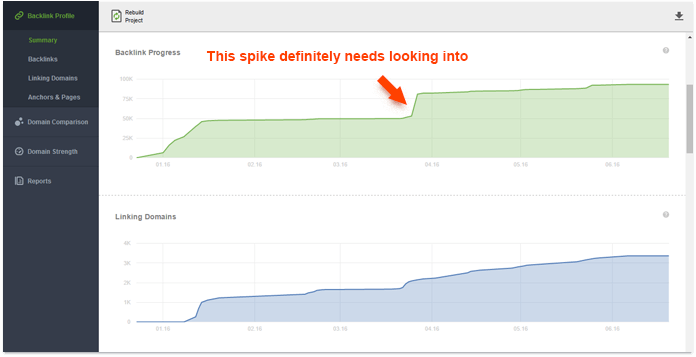
2. Check for penalty risks. The stats that Penguin likely looks at are incorporated into SEO SpyGlass and its Penalty Risk formula, so instead of looking at each individual factor separately, you can weigh them as a whole, pretty much like Google does.
In your SEO SpyGlass project, switch to the Linking Domains dashboard and navigate to the Link Penalty Risks tab. Select all domains on the list, and click Update Link Penalty Risk. Give SEO SpyGlass a minute to evaluate all kinds of quality stats for each one of the domains. When the check is complete, examine the Penalty Risk column, and make sure to manually look into every domain with a Penalty Risk value over 50%.

If you use SEO SpyGlass' free version, you'll get to analyze up to 1,000 links; if you're looking to audit more links, you'll need a Professional or Enterprise license.
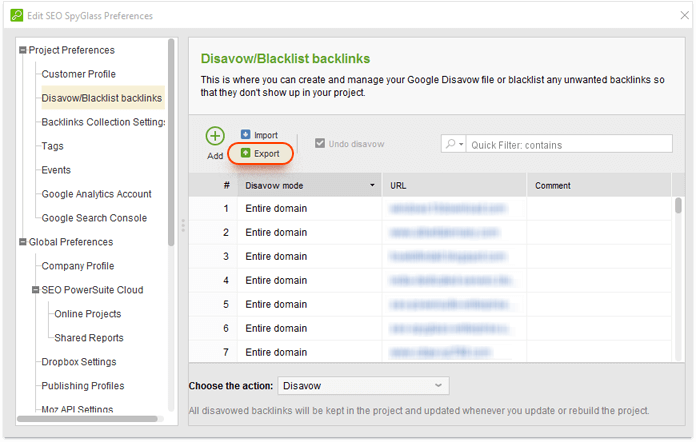
3. Get rid of harmful links. Ideally, you should try to request removal of the spammy links in your profile by contacting the webmasters of the linking sites. But if you have a lot of harmful links to get rid of, or if you don't hear back from the webmasters, it's a good idea to disavow the links using Google's Disavow tool. This way, you'll be telling Google to ignore those links when evaluating your link profile. Disavow files can be tricky in terms of syntax and encoding, but SEO SpyGlass can automatically generate them for you in the right format.
In your SEO SpyGlass project, select the links you're about to disavow, right-click the selection, and hit Disavow backlinks. Select the disavow mode for your links (as a rule of thumb, you'd want to disavow entire domains rather than individual URLs). Once you've done that for all harmful links in your project, go to Preferences > Blacklist/Disavow backlinks, review your list, and hit Export to save the file to your hard drive. Finally, upload the disavow file you just created to Google's Disavow tool.
3. Pirate

Launched: Aug 2012
Rollouts: Oct 2014
Goal: De-rank sites with copyright infringement reports
Rollouts: Oct 2014
Goal: De-rank sites with copyright infringement reports
Hazards
- Pirated content
- High volume of copyright infringement reports
How to stay safe
Don't distribute anyone's content without the copyright owner's permission. Really, that's it.4. Hummingbird

Launched: August 22, 2013
Rollouts: —
Goal: Produce more relevant search results by better understanding the meaning behind queries
Rollouts: —
Goal: Produce more relevant search results by better understanding the meaning behind queries
While keywords within the query continue to be important, Hummingbird adds more strength to the meaning behind the query as a whole. The use of synonyms has also been optimized with Hummingbird; instead of listing results with the exact keyword match, Google shows more theme-related results in the SERPs that do not necessarily have the keywords from the query in their content.
Hazards
- Exact-match keyword targeting
- Keyword stuffing
How to stay safe
1. Expand your keyword research. With Hummingbird, it's a good idea to focus on related searches, synonyms and co-occurring terms to diversify your content, instead of relying solely on short-tail terms you'd get from Google AdWords. Great sources of Hummingbird-friendly keyword ideas are Google Related searches, Google Autocomplete, and Google Trends. You'll find all of them incorporated into SEO PowerSuite's Rank Tracker.To start expanding your list of target keywords, open Rank Tracker and create or open a project. Go to the Keyword Research module and click Suggest keywords. Select Google Autocomplete as your research method.
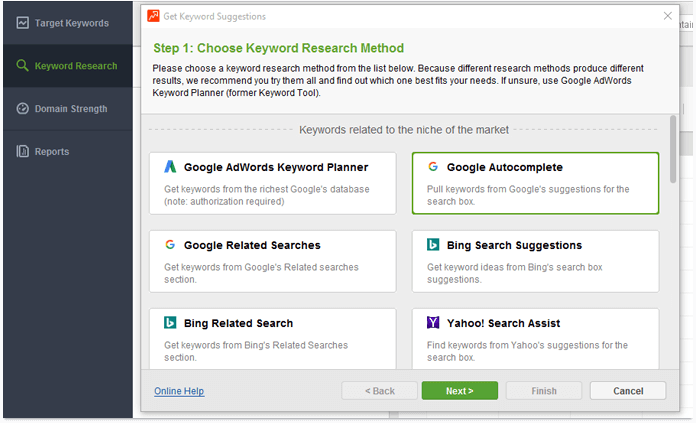
Enter the seed terms to base your research upon, and hit Next. Hang on while Rank Tracker is pulling suggestions for you, and click Finish when it's done to add the just found keyword ideas to your project. Then go through the process again, this time selecting Google Related Searches as your research method. Do the same for Google Trends. Next, proceed with analyzing the keywords' efficiency and difficulty, and pick the top terms to map them to landing pages.
2. Discover the language your audience uses. It's only logical that your website's copy should be speaking the same language as your audience, and Hummingbird is yet another reason to step up the semantic game. A great way to do this is by utilizing a social media listening tool (like Awario) to explore the mentions of your keywords (your brand name, competitors, industry terms, etc.) and see how your audience is talking about those things across social media and the Web at large.
3. Ditch exact-match, think concepts. Unnatural phrasing, especially in titles and meta descriptions, is still popular among websites, but with search engines' growing ability to process natural language, it can become a problem. If you are still using robot-like language on your pages for whatever reason, now (or, to be honest, four years ago) is the time to stop.
Including keywords in your title and description still matters; but it's just as important that you sound like a human. As a nice side effect, improving your title and meta description is sure to increase the clicks your Google listing gets.
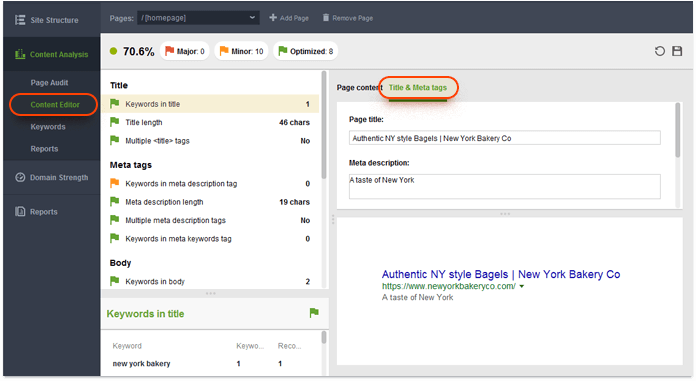
To play around with your titles and meta descriptions, use SEO PowerSuite's WebSite Auditor. Run the tool, create or open a project, and navigate to the Pages module. Go through your pages' titles and meta descriptions and spot the ones that look like they were created purely for search engine bots. When you spot a title you'd like to correct, right-click the page and hit Analyze page content. When the analysis is complete, go to Content Editor, switch to the Title & Meta tags tab, and rewrite your title and/or meta description. Right below, you'll see a preview of your Google snippet.
5. Pigeon

Launched: July 24, 2014 (US)
Rollouts: December 22, 2014 (UK, Canada, Australia)
Goal: Provide high quality, relevant local search results
Rollouts: December 22, 2014 (UK, Canada, Australia)
Goal: Provide high quality, relevant local search results
Pigeon led to a significant (at least 50%) decline in the number of queries local packs are returned for, gave a ranking boost to local directory sites, and connected Google Web search and Google Map search in a more cohesive way.
Hazards
- Poorly optimized pages
- Improper setup of a Google My Business page
- NAP inconsistency
- Lack of citations in local directories (if relevant)
How to stay safe
1. Optimize your pages properly. Pigeon brought in the same SEO criteria for local listings as for all other Google search results. That means local businesses now need to invest a lot of effort into on-page optimization. A good starting point is running an on-page analysis with SEO PowerSuite's WebSite Auditor. The tool's Content Analysis dashboard will give you a good idea about which aspects of on-page optimization you need to focus on (look for the factors with the Warning or Error statuses). Whenever you feel like you could use some inspo, switch to the Competitors tab to see how your top ranking competitors are handling any given part of on-page SEO.
For a comprehensive guide to on-page optimization, check out the on-page section of SEO Workflow.
2. Set up a Google My Business page. Creating a Google My Business page for your local biz is the first step to being included in Google's local index. Your second step will be to verify your ownership of the listing; typically, this involves receiving a letter from Google with a pin number which you must enter to complete verification.
As you set up the page, make sure you categorize your business correctly — otherwise, your listing will not be displayed for relevant queries. Remember to use your local area code in the phone number; the area code should match the code traditionally associated with your location. The number of positive reviews can also have an influence on local search rankings, so it's a good idea to encourage happy customers to review your place.
3. Make sure your NAP is consistent across your local listings. Google will be looking at the website you've linked to from your Google My Business page and cross-reference the name, address and phone number of your business. If all elements match, you're good to go.
If your business is also featured in local directories of any kind, make sure the business name, address, and phone number are also consistent across these listings. Different addresses listed for your business on Yelp and TripAdvisor, for instance, may put your local rankings to nowhere.
4. Get featured in relevant local directories. Local directories, like Yelp, TripAdvisor and the like, have seen a major ranking boost after Pigeon. So while it may be harder for your site to rank within the top results now, it's a good idea to make sure you are featured in the business directories that will likely rank high. You can easily find quality directories and reach out to webmasters to request a feature with SEO PowerSuite's link building tool, LinkAssistant.
Launch LinkAssistant and open or create a project for your site. Click Look for prospects in the top left corner and pick Directories as your research method.
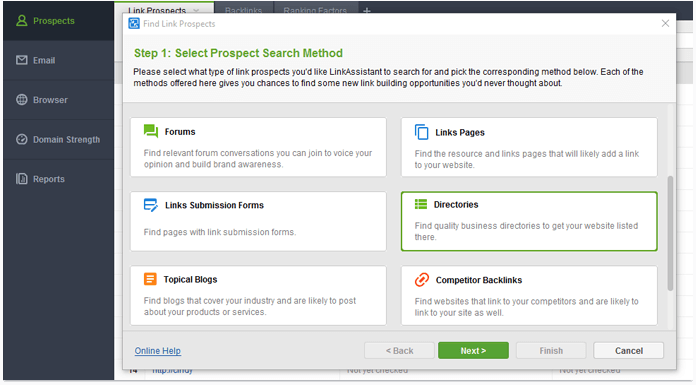
Enter your keywords — it's a good idea to specify category keywords plus your location (e.g. "dentist Denver") — and give the tool a sec to find the relevant directories in your niche.
In a minute, you'll see a list of directories along with the webmasters' contact email addresses. Now, pick one of the directories you'd like to be included in, right-click it, and hit Send email to selected partner. Set up your email prefs, compose the message (or pick a ready-made email template), and send it off!
6. Mobile Friendly Update

Launched: April 21, 2015
Rollouts: —
Goal: Give mobile friendly pages a ranking boost in mobile SERPs, and de-rank pages that aren't optimized for mobile
Rollouts: —
Goal: Give mobile friendly pages a ranking boost in mobile SERPs, and de-rank pages that aren't optimized for mobile
Mobile friendliness is a page-level factor, meaning that one page of your site can be deemed mobile friendly and up-ranked, while the rest might fail the test.
Hazards
- Lack of a mobile version of the page
- Improper viewport configuration
- Illegible content
- Plugin use
How to stay safe
1. Go mobile, cap. C'mon, it's been 2 years since Mobilegeddon. There are a few mobile website configurations to choose from, but Google's recommendation is responsive design. Google also has specific mobile how-tos for various website platforms to make going mobile easier for webmasters.2. Take the mobile friendly test. Going mobile isn't all it takes — you must also pass Google's mobile friendliness criteria to get up-ranked in mobile SERPs. Google's mobile test in integrated into SEO PowerSuite's WebSite Auditor so you can check your pages' mobile friendliness quickly.
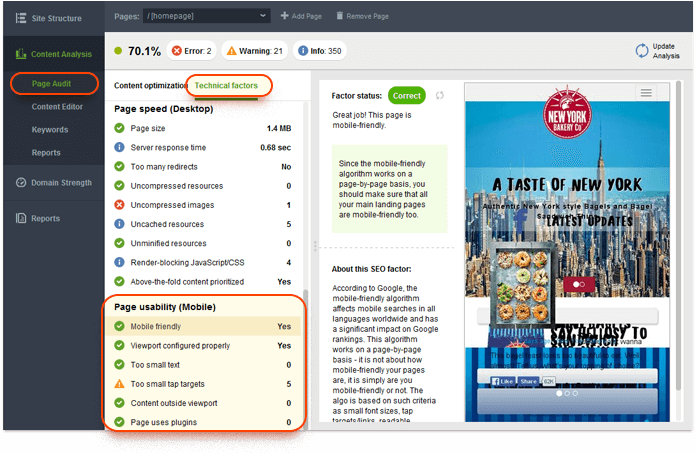
Launch WebSite Auditor and open your project. Go to Content Analysis and click Add page to pick a page to be analyzed. Enter your target keywords and give the tool a moment to run a quick page audit. When the audit is complete, switch to Technical factors on the list of SEO factors on the left, and scroll down to the Page usability (Mobile) section.
The Mobile friendly factor will show you whether or not your page is considered mobile friendly overall; here, you also get a mobile preview of your page. The factors below will indicate whether your page meets all of Google's mobile friendliness criteria. Click on any factor with an Error or Warning status for specific how-to fix recommendations.
7. RankBrain

Launched: October 26, 2015 (possibly earlier)
Rollouts: —
Goal: Deliver better search results based on relevance & machine learning
Rollouts: —
Goal: Deliver better search results based on relevance & machine learning
While there is a query processing component in RankBrain, there also is a ranking component to it (when RankBrain was first announced, Google called it the third most important ranking factor). Presumably, RankBrain can somehow summarize what a page is about, evaluate the relevancy of search results, and teach itself to get even better at it with time.
The common understanding is that RankBrain, in part, relies on the traditional SEO factors (links, on-page optimization, etc.), but also looks at other factors that are query-specific. Then, it identifies the relevance features on the pages in the index, and arranges the results respectively in SERPs.
Hazards
- Lack of query-specific relevance features
- Poor user experience
How to stay safe
1. Maximize user experience. Of course, RankBrain isn't the reason to serve your visitors better. But it's a reason why not optimizing for user experience can get you down-ranked in SERPs.Keep an eye on your pages' user experience factors in Google Analytics, particularly Bounce Rate and Session Duration. While there are no universally right values to stick by, here are the averages across various industries reported by KissMetrics (you can find the complete infographic here).
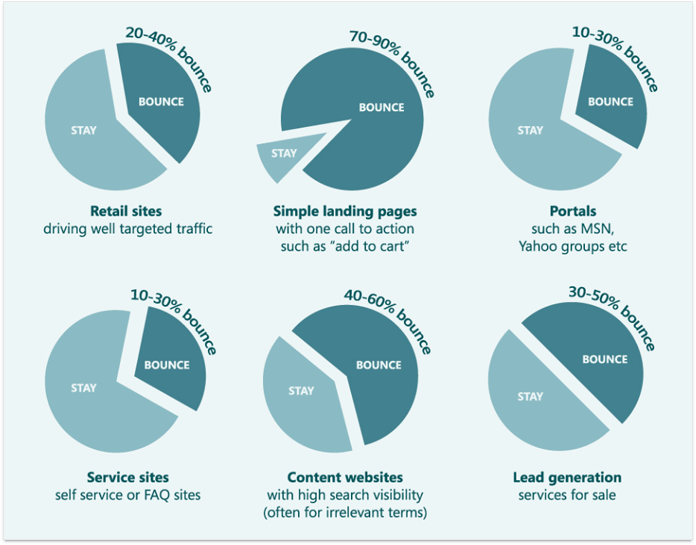
If your bounces for some of the pages are significantly above these averages, those are the low-hanging fruit to work on. Consider A/B testing different versions of these pages to see which changes drive better results.
As for session duration, keep in mind that the average reading speed (for readers who skim) is 650 words per minute. Use this as guidance in assessing the amount of time visitors spend on your pages, and see if you can improve that by diversifying your content, such as including more images and videos. Additionally, examine the pages that have the best engagement metrics, and use takeaways in crafting your next piece of content.
2. Do competition research. One of the things RankBrain is believed to do is identify query-specific relevance features of webpages, and use those features as signals for ranking pages in SERPs. Such features can be literally anything on the page that can have a positive effect on user experience. To give you an example, pages with more content and more interactive elements may be more successful.
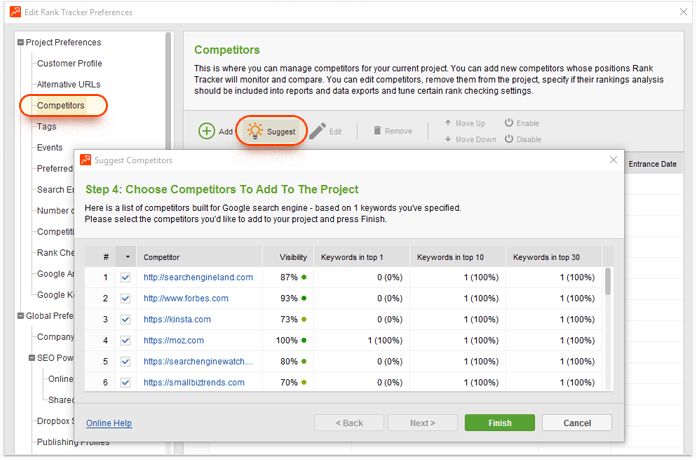
While there is no universal list of such features, you can get a good idea of what they may be by analyzing the common traits of your top ranking competitors. Start SEO PowerSuite's Rank Tracker and go to Preferences > Competitors. Click Suggest, and enter your target keywords (you can — and should — make the list long, but make sure you only enter the terms that belong to one topic at a time). Rank Tracker will now look up all the terms you entered and come up with 30 sites that rank in Google's top 30 most often. When the search is complete, choose up to 10 of those to add to your project, examine their pages in-depth, and look for relevance features you may want to incorporate on your site.
8. Possum

Launched: September 1, 2016
Rollouts: —
Goal: Deliver better, more diverse results based on the searcher's location and the business' address
Rollouts: —
Goal: Deliver better, more diverse results based on the searcher's location and the business' address
Hazards
- Sharing a physical address with a similar business
- Competitors whose business address is closer to the searcher's location
How to stay safe
1. Do geo-specific rank tracking. After Possum, the location from which you're checking your rankings plays an even bigger part in the results you get. If you haven't done this yet, now is the time to set up a custom location to check positions from in SEO PowerSuite's Rank Tracker. To get started, open the tool, create a project for your site, and press Add search engines at Step 4. Next to Google (or Google Maps, if that's what you're about to track), click Add Custom. Next, specify the Preferred location (since Possum made the searcher's location so important, it's best to specify something as specific as a street address or zip code):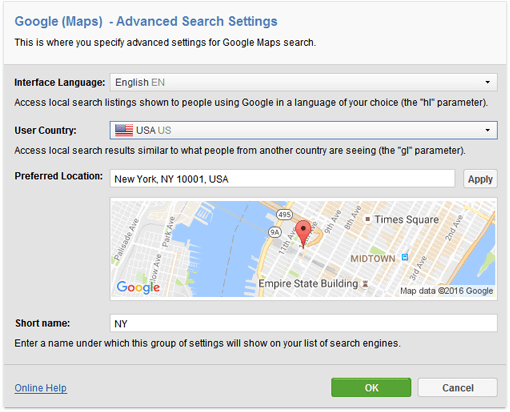
You can always modify the list of the local search engines you're using for rank checking in Preferences > Preferred Search Engines.
2. Expand your list of local keywords. Since Possum resulted in greater variety among the results for similar-looking queries, it's important that you track your positions for every variation separately.
To discover those variations, open SEO PowerSuite's Rank Tracker and create or open a project. Go to the Keyword Research module and click Suggest keywords. Enter the localized terms you are already tracking and hit Next. Select Google Autocomplete as your research method.
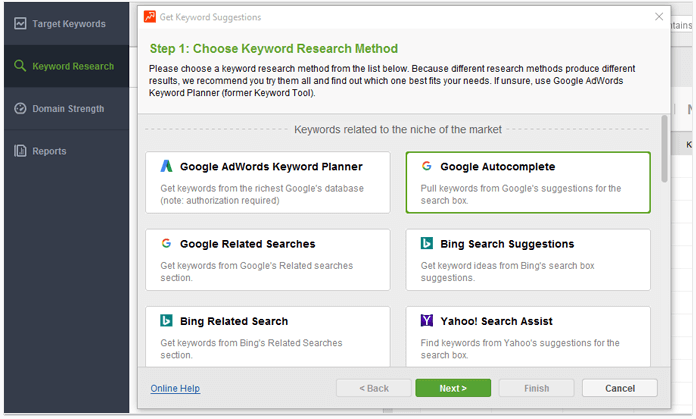
This should give you an ample list of terms that are related to the original queries you specified. You may also want to repeat the process for other methods, particularly Google Related Searches and Google Trends for even more variations.
Overall, with the Possum update, it's becoming even more important to optimize your listings specifically for local search. For a full list of local ranking factors and how-to tips, jump here.
9. Fred

Launched: March 8, 2017
Rollouts: —
Goal: Filter out low quality search results whose sole purpose is generating ad and affiliate revenue
Rollouts: —
Goal: Filter out low quality search results whose sole purpose is generating ad and affiliate revenue
Hazards
- Low-value, ad-centered content
- Thin, affiliate-heavy content
How to stay safe
1. Review Google's guidelines. This may seem a tad obvious, but reviewing the Google Webmaster guidelines and Google Search Quality Guidelines (particularly the latter) is a good first step in keeping your site safe from Fred.2. Watch out for thin content. Look: New York Times, the Guardian, and Huffington Post all show ads — literally every publisher site does. So it's not the ads that Fred targets; it's the content. Audit your site for thin content, and update the low quality, low word count pages with relevant, useful information.
To start the check, navigate to the Pages module in SEO PowerSuite's WebSite Auditor and look for the Word count column. Now, sort the pages by their word count by clicking on the column's header to instantly spot pages with too little content.
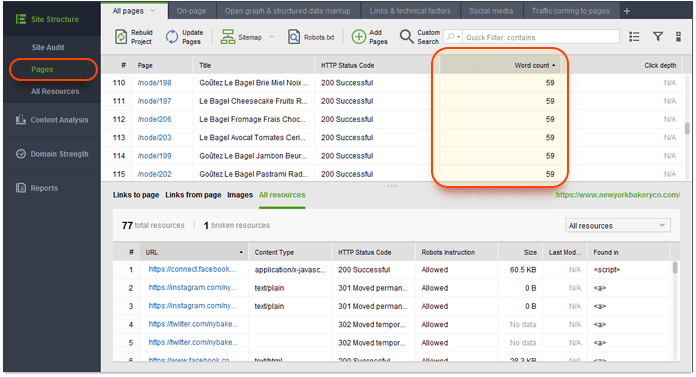
But remember: short pages can do perfectly fine for certain queries. To see if your content length is within a reasonable range for your target keywords, go to Content Analysis and select the page you'd like to analyze. Enter the keyword, and hang on a sec while Google examines your and your top ranking competitors' pages. When the analysis is complete, look at Word count in body. Click on this factor and see how long the competitors' pages are.
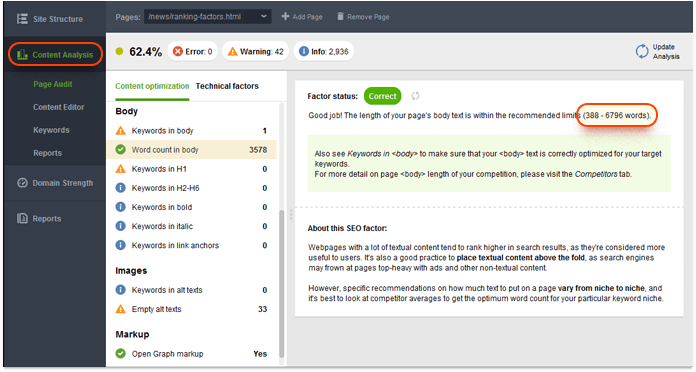
To see each individual competitor's content length, click on Keywords in body and switch to Competitors. Here, you'll get a list of your top 10 competitors for the keywords you specified, along with the total word count on each of these pages. This should give you a solid idea on approximately how much content the searchers are looking for when they search for your target keywords.
Reference: https://www.link-assistant.com/news/google-algorithm-updates.html